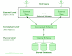
Merge Sort is a divide and conquer algorithm that was invented by John von Neumann in 1945.
Conceptually, a merge sort works as follows:
Conceptually, a merge sort works as follows:
- Divide the unsorted list into n sublists, each containing 1 element (a list of 1 element is considered sorted).
- Repeatedly merge sublists to produce new sorted sublists until there is only 1 sublist remaining. This will be the sorted list.
EXAMPLE
Reference: Wikipedia
MERGE SORT C-CODE
// C program for implementation of Merge sort
#include <stdio.h>
// Merges two subarrays of arr[].
// First subarray is arr[l..m]
// Second subarray is arr[m+1..r]
void merge(int arr[], int l, int m, int r)
{
int i, j, k;
int n1 = m - l + 1;
int n2 = r - m;
/* create temp arrays */
int L[n1], R[n2];
/* Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[] */
for (i = 0; i < n1; i++)
L[i] = arr[l + i];
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++)
R[j] = arr[m + 1+ j];
/* Merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r]*/
i = 0; // Initial index of first subarray
j = 0; // Initial index of second subarray
k = l; // Initial index of merged subarray
while (i < n1 && j < n2)
{
if (L[i] <= R[j])
{
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
}
else
{
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
// Copy the remaining elements of L[], if there are any
while (i < n1)
{
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
k++;
}
// Copy the remaining elements of R[], if there are any
while (j < n2)
{
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
/* l is for lower index and u is upper index of the
sub-array of arr to be sorted */
void mergeSort(int arr[], int l, int u)
{
if (l < u)
{
// Same as (l+u)/2, but avoids overflow for
// large l and h
int m = l+(u-l)/2;
// Sort first and second halves
mergeSort(arr, l, m);
mergeSort(arr, m+1, u);
merge(arr, l, m, u);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {6, 3, 5, 2, 8, 10, 9};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int i, j,temp;
//Merge Sort calling
mergeSort(arr, 0, n - 1);
printf("Sorted array: \n");
for (int i=0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
COMPLEXITY ANALYSIS
- Best, Average and Worst Case Time Complexity: O(nLog(n) ).
- Auxiliary Space Complexity: O(n).